News
RIPK to to Achieve a Happy Indonesia
Front Row (The Jakarta Post) October 28, 2024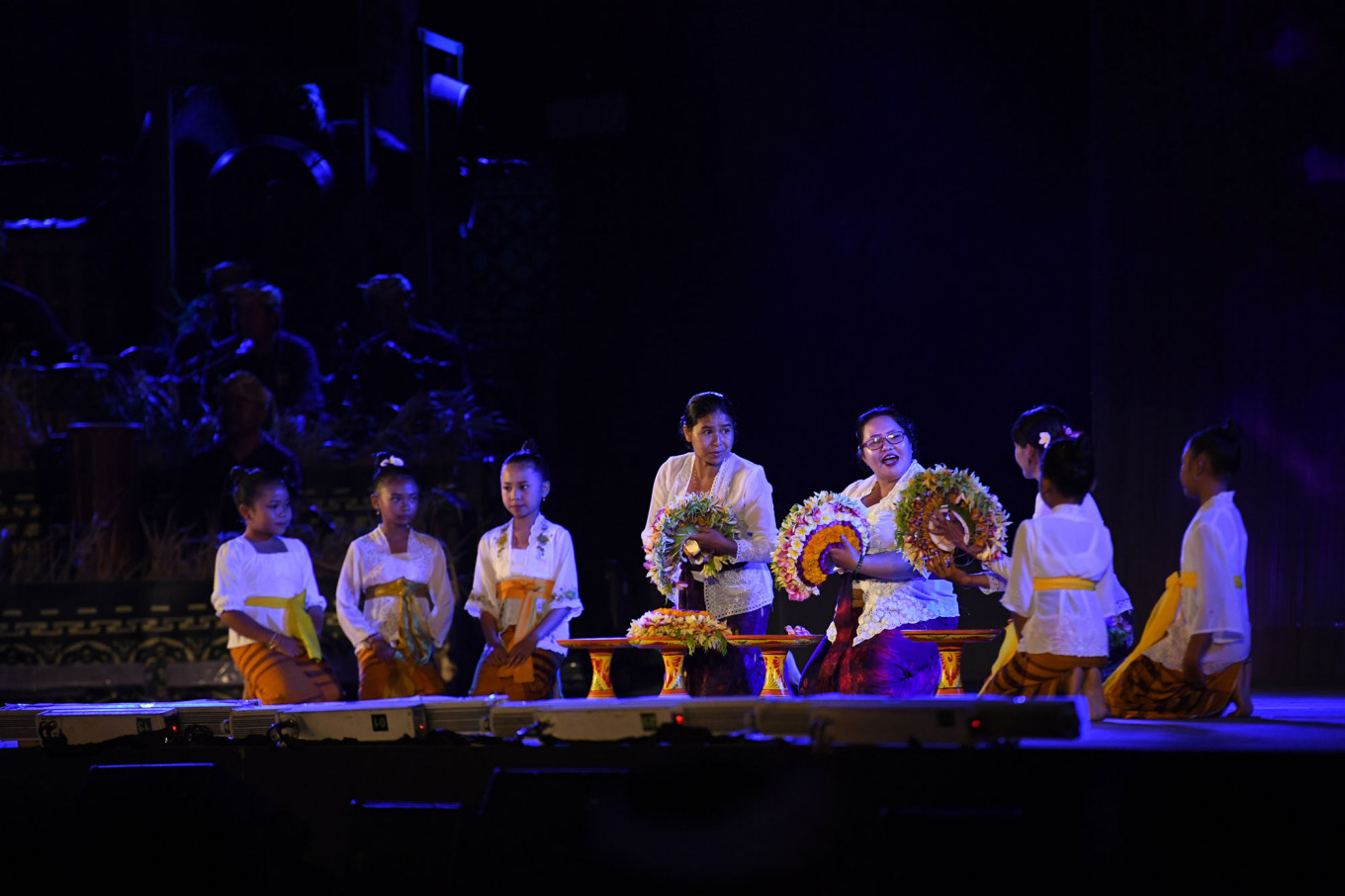 (Kemendikbudristek)
(Kemendikbudristek)
President Joko "Jokowi" Widodo has signed Presidential Regulation (Perpres) No. 115/2024 concerning the Master Plan for Cultural Advancement (RIPK) for the 2025-2045 period. This policy marks a significant milestone in the development of national culture, integrating culture as a key pillar in creating a prosperous and happy Indonesia.
Education, Culture, Research, and Technology Ministry (Kemendikbudristek) Culture Director-General Hilmar Farid emphasized the importance of this policy in addressing the challenges of globalization and changing times.
"The RIPK 2025-2045 is not just about preserving cultural heritage but also utilizing culture as a driving force for the welfare of society," he stated at Kemendikbudristek office in Jakarta on Oct. 14, 2024.
According to Hilmar, this regulation responds to the need for a long-term cultural strategy document, focusing not only on preserving cultural heritage but also on developing culture as a means to strengthen national identity and enhance Indonesia’s global contribution. This aligns with the mandate of Article 32 of the 1945 Constitution and Law No. 5/2017 on the Advancement of Culture.
The RIPK outlines a grand vision of "A Happy Indonesia Based on Cultural Diversity that Enlightens, Brings Peace, and Prosperity," highlighting culture as a national asset that must be safeguarded, developed, and optimally utilized for the welfare of society.
"This vision is highly relevant to our current needs, where cross-cultural interactions and the use of culture for international diplomacy are becoming increasingly crucial," Hilmar Farid added.
The 2025-2045 Master Plan for Cultural Advancement carries seven main missions. First, it provides space for diverse cultural expressions and promotes cross-group cultural interactions to strengthen inclusive culture. Second, it protects and develops traditional cultural values and expressions so that national culture continues to be enriched by ancestral heritage. Third, it leverages cultural wealth to improve Indonesia's standing on the global stage, particularly through cultural diplomacy.
Fourth, it uses the objects of Cultural Advancement as a means to improve societal welfare, especially through the development of the creative economy and culture-based tourism. Fifth, it promotes culture that protects biodiversity and strengthens the cultural ecosystem in the context of environmental sustainability.
Sixth, it encourages institutional and budgeting reforms to support the more effective and efficient advancement of culture. Seventh, it enhances the role of the government as a facilitator of Cultural Advancement, allowing for active public participation.
"This Perpres on the RIPK provides a crucial framework for formulating cultural policies over the next 20 years," said the Director-General.
An essential aspect of the RIPK is the emphasis on three main policy directions in Cultural Advancement: ensuring the freedom of the public to preserve and develop cultural values in a participatory and inclusive manner, managing Objects of Cultural Advancement (OPK) and cultural heritage sustainably as the foundation for improving public welfare and Indonesia's cultural influence globally, and improving the quality of government governance as a facilitator of cultural advancement.
Each of these policy directions is detailed through concrete strategies to be implemented gradually, including enhancing support for cultural communities, developing traditional cultures in harmony with modern culture, and improving the quality of cultural services and infrastructure.
The RIPK will also be implemented through the National Cultural Advancement Action Plan (RAN) updated every five years. One key innovation in executing this policy is the use of the Cultural Development Index (IPK) as a measure of success. In 2023, Indonesia's IPK reached 57.13 points, with a target of increasing to 68.15 points by 2045.
"This index is an important benchmark to assess how well cultural policies can address the challenges of the times and societal needs. We are optimistic that this target can be achieved," Hilmar Farid explained.
Through Perpres No. 115/2024, regional governments are also encouraged to play an active role in developing cultural programs aligned with national policies. The active participation of the public and cultural communities will be key to the successful implementation of this master plan.
Through close collaboration between the government, the public, and all stakeholders, it is hoped that the 2025-2045 RIPK will realize culture as a driving force for inclusive and sustainable development.
Source: www.thejakartapost.com